“To be a better girl ”
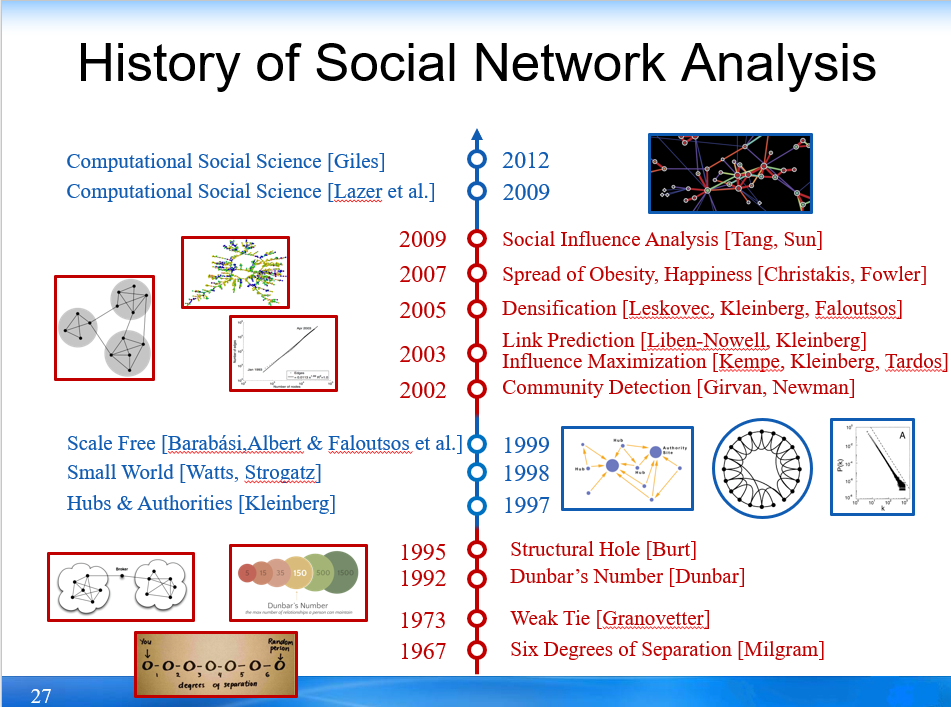
1. History of SNA
1.1. Background
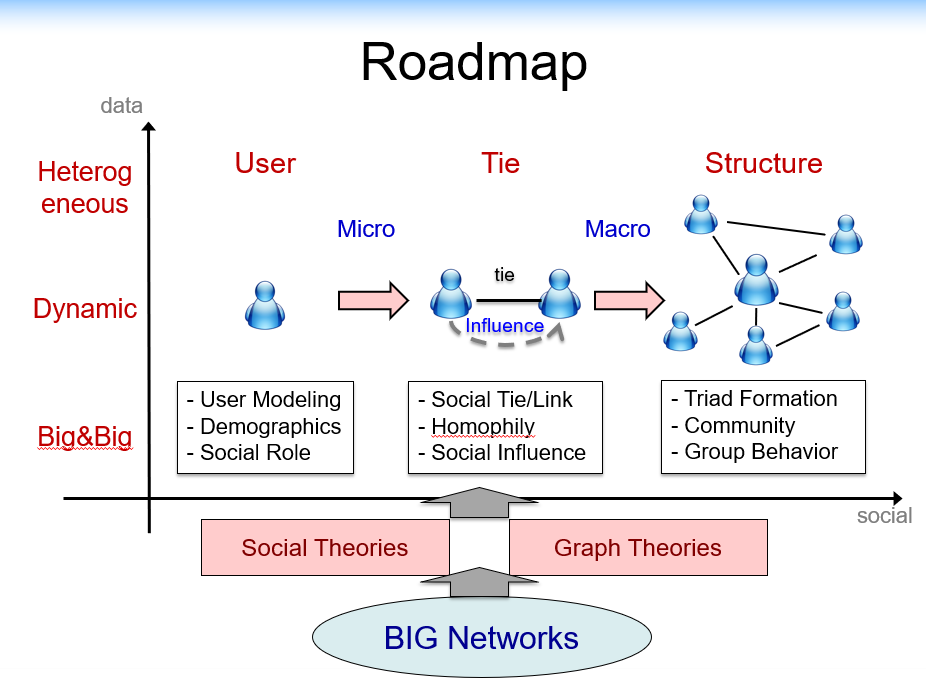
1.2. Roadmap
1.3. Example
- Example in AMiner
- Expert Search
- Researcher Profile
- Collaboration Recommendation
-
sparse connection
比较难找到跨学科的合作者
-
topic skewness
not all topics are relevant for crossdomain collaborations
-
- Reviewer Suggestion
2. Social Tie and Social Influence
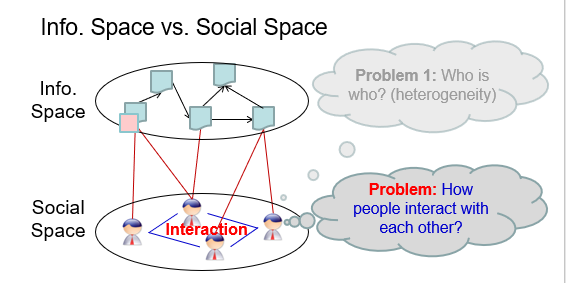
- finding boss in email networks
-
finding friends in mobile networks
挑战:
- 背后的作用力(fundamental forces )
- 是否可以自动推断社会纽带类型
2.1. social tie
Problem Formulation
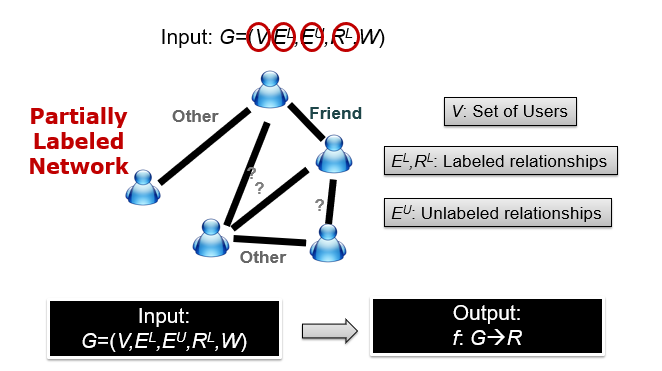
-
input–social network(partially labeled)
包含用户集合,部分标记
-
objective–learn a mapping function(predict the relationship semantics)
不仅要考虑已标记信息,也要考虑未标记的网络结构
basic idea
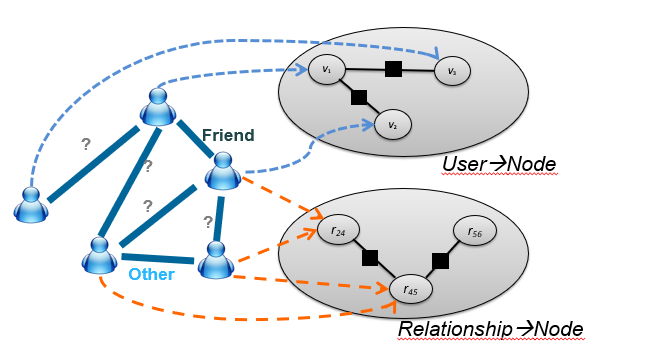 two ways
two ways
- model each user as a node
- model each relationship as a node
第一种更加直观,但难以描述不同关系间的关系
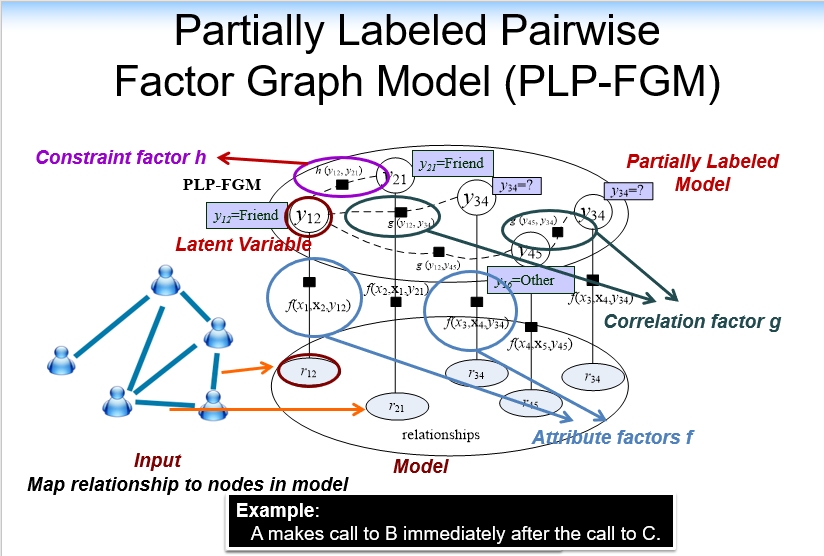 目标: 对于每一个关系,识别最有可能的类型
目标: 对于每一个关系,识别最有可能的类型
- 左边为input,右边是模型
- 对每一个关系节点,都有一个相关潜在变量y,表示该关系的类型
- 三个因子
- is attribute factor
- correlation factor
- constraint factor
solutions
- exponential-linear functions
- Log-Likelihood of labeled Data
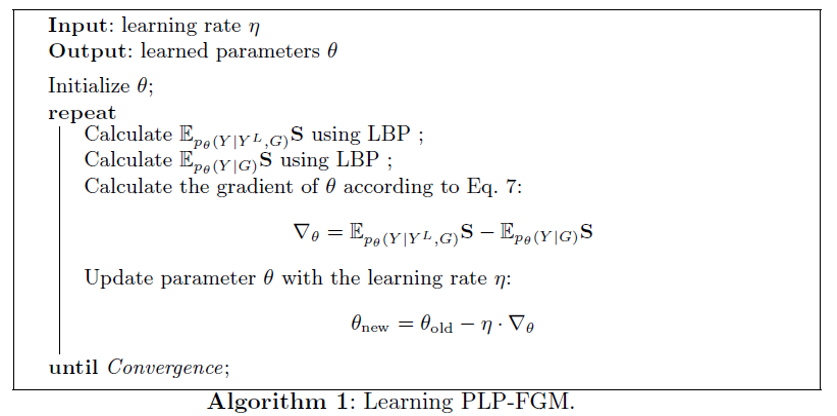
challenge
- 更有效的训练数据
- 从其他网络借鉴
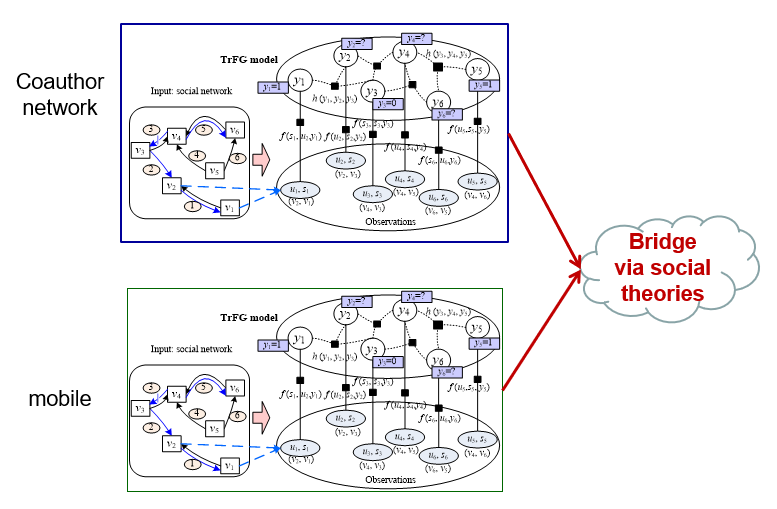
2.2. Inferring Social Ties across Heterogeneous Networks
social theories
- social balance theory
- structural hole theory
- social status theory
- two-step-flow theory
2.3. Peer Influence
- Formulation: Topic-based Social Influence Analysis
- The Solution: Topical Affinity Propagation
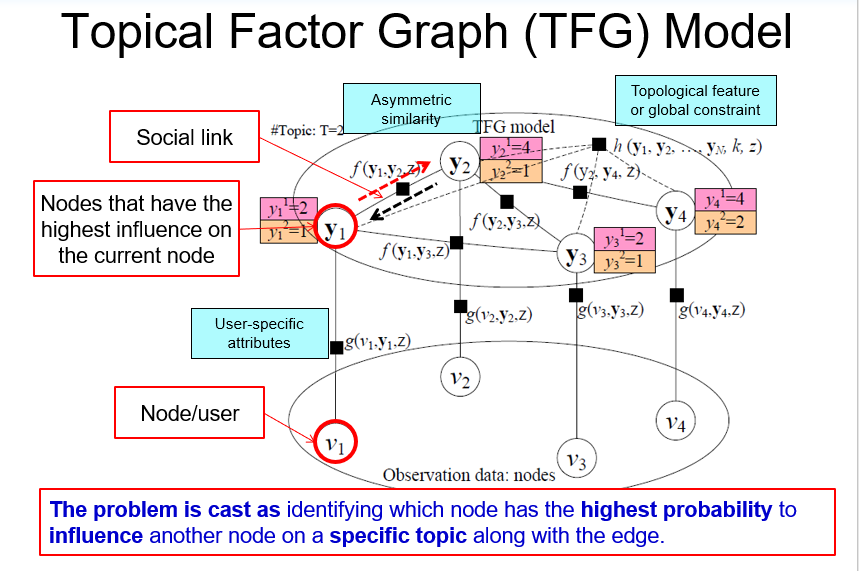
- The Solution: Topical Affinity Propagation
2.4. Structural Influence
Influence
- Peer influence
- Conformity influence
- Individual influence
3. Group and Structure
- Group Lyfecyle
- Structural Hole in Diffusion
Computational Models for Social Network Analysis